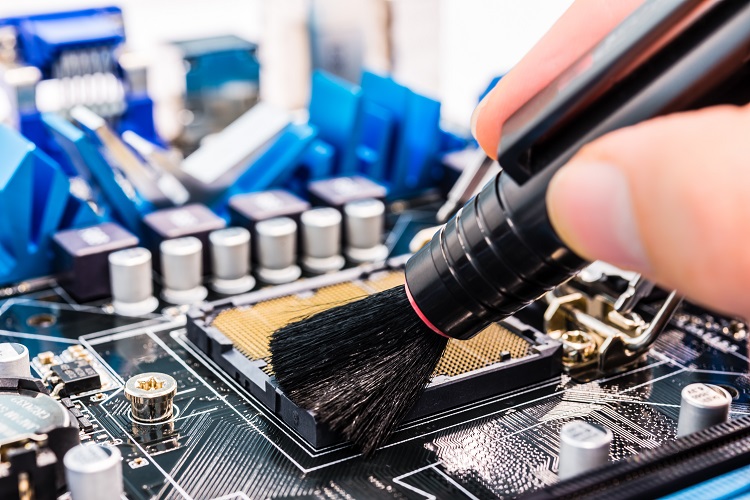
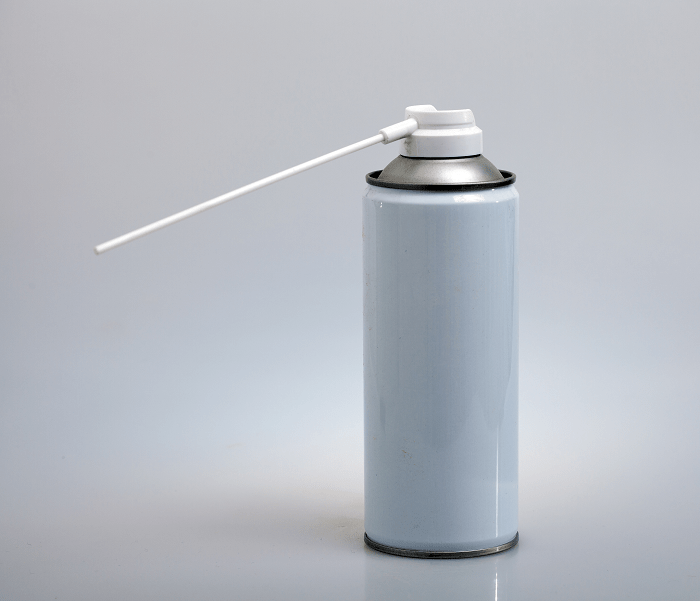
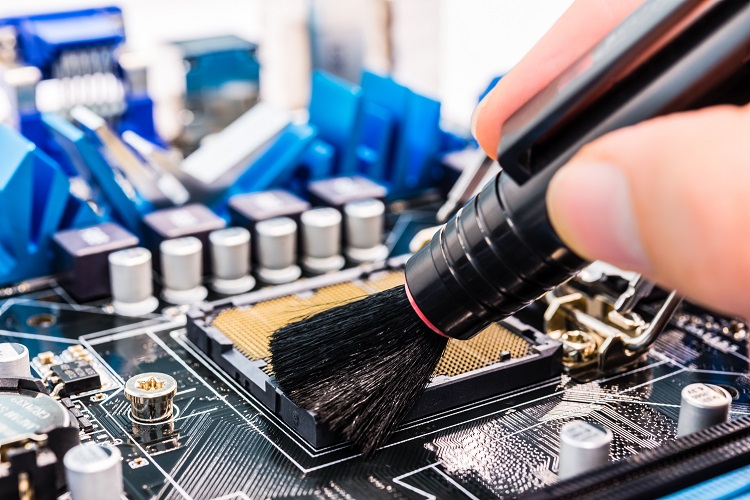
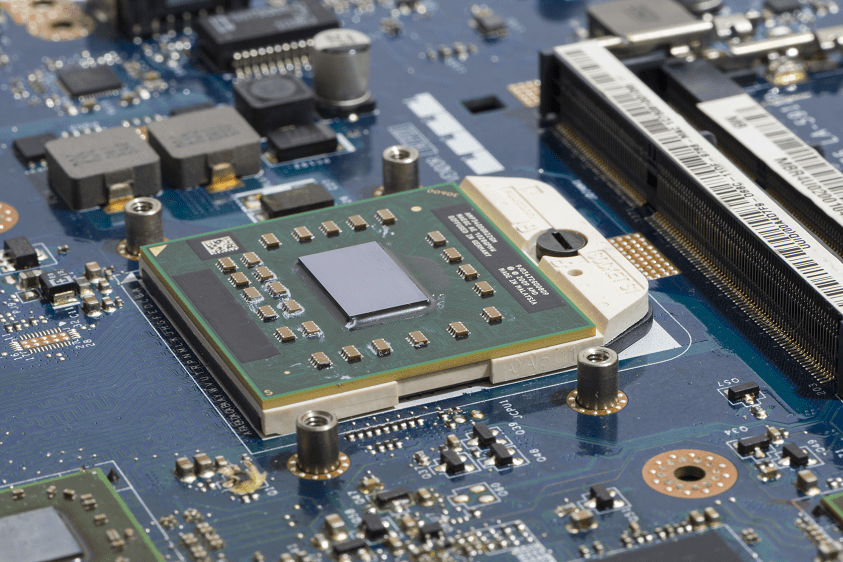
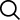When circuit boards are assembled, the parts comprising the circuit board are soldered to minimize and eliminate the potential for damage. In order for the solder to make a perfect connection to the parts and to the board, a substance called flux is mixed into the...