Electrically powered machinery plays a vital role in businesses and product production. For this machinery to operate, electrical contacts are...
Blog

CHEMICAL INDUSTRY NEWS
Chemical Chat – Discover What’s New!
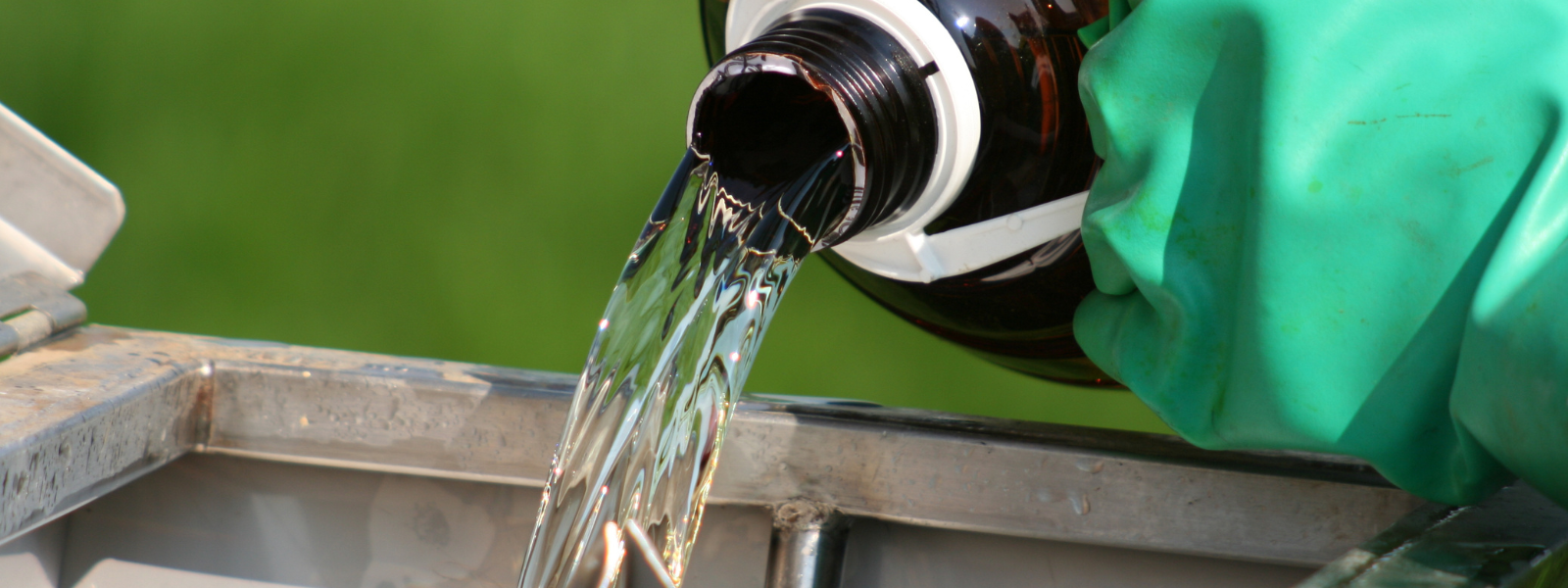
Recycle Solvent: Sustainable Practices in Industrial Cleaning
Sustainability is a key focus for industries looking to reduce their environmental impact and embrace eco-friendly practices. In the industrial...
Proper Handling and Waste Management
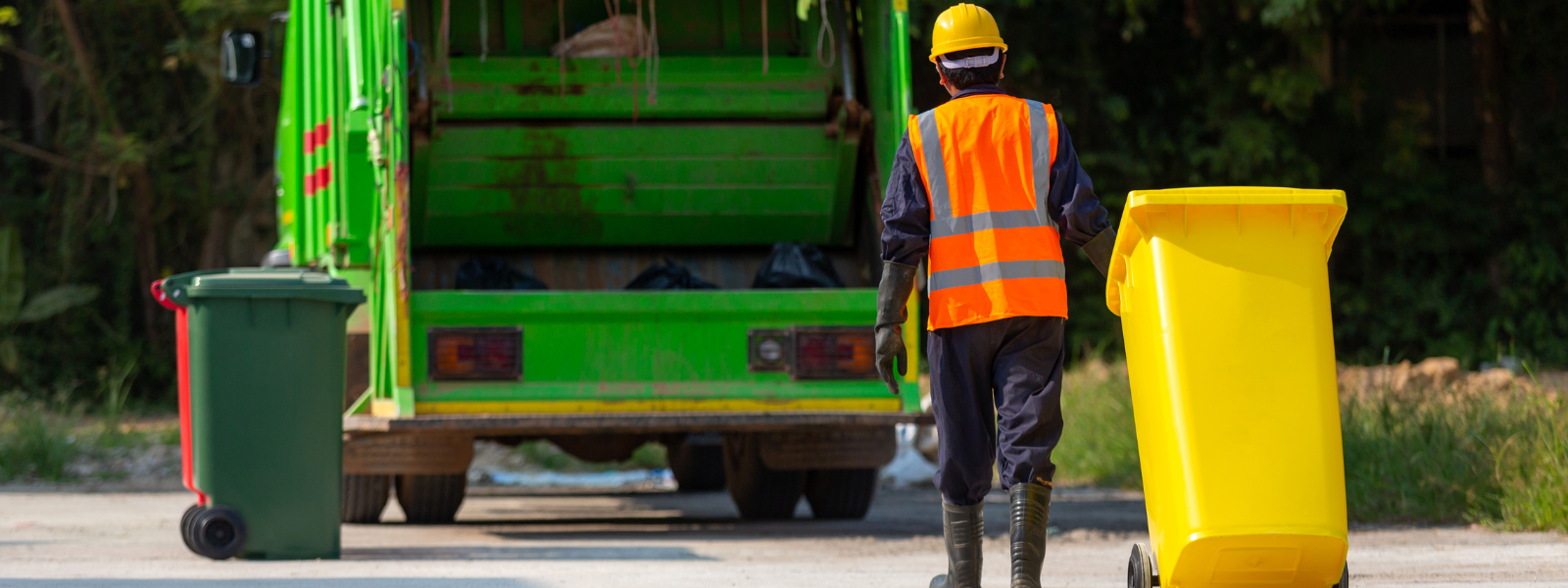
Many solvents are utilized in industrial settings daily. However, with solvents used often in processes and products, what is done to the waste...
How to Dispose of Solvents: Safe and Responsible Methods
Proper disposal of solvents is a crucial aspect of responsible waste management for businesses. Solvents are often...
Recycle Solvent: Sustainable Practices in Industrial Cleaning
Sustainability is a key focus for industries looking to reduce their environmental impact and embrace eco-friendly...
Company News

Managed Services
Discover the Latest in Safe and Sustainable Chemical Solutions
Stay informed with Ecolink’s blog! Subscribe now
Chemical Management Information
Stay updated with us
Sign Up for the Latest Updates
Stay informed about chemical supply chain disruptions and emerging innovations to keep your business at the forefront of efficiency and innovation. Uncover new ways to make your business practices more sustainable by incorporating safer products into your cleaning lineup.