For many business operations, a well-maintained fleet of vehicles is not only a functional necessity; it is a reflection of a company’s commitment...
Blog

CHEMICAL INDUSTRY NEWS
Chemical Chat – Discover What’s New!
Understanding the EPA’s TCE Ban & Safer Alternatives with Ecolink
What is the EPA TCE Ban? The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has finalized a rule banning the use of trichloroethylene (TCE), a chemical...
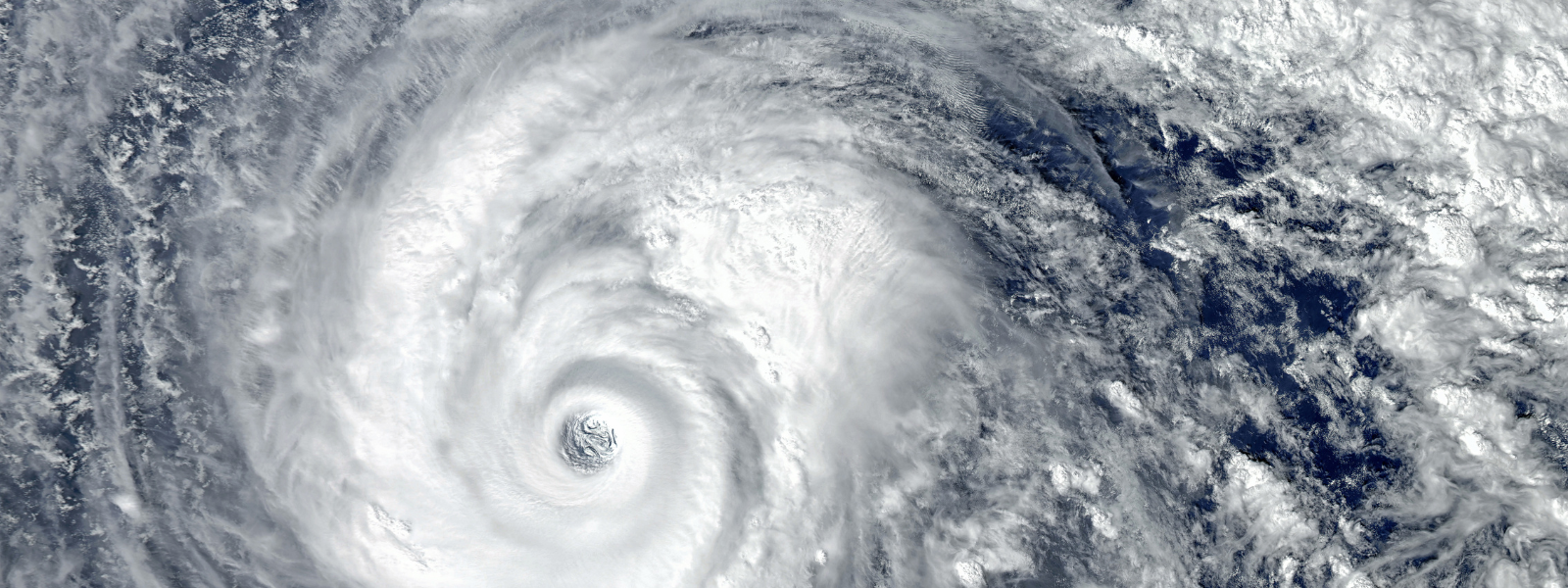
D-Limonene Production Disruptions: The Impact of Hurricane Milton
SHOP NOW The effects of Hurricane Milton are currently being felt throughout the global supply chain, especially when it comes to chemicals...
What is the best solvent to dissolve grease?
Not sure what is the best solvent to dissolve grease? Choosing the right solvent can either lead to a...
Understanding the EPA’s TCE Ban & Safer Alternatives with Ecolink
What is the EPA TCE Ban? The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has finalized a rule banning the use of...
Company News

Managed Services
Discover the Latest in Safe and Sustainable Chemical Solutions
Stay informed with Ecolink’s blog! Subscribe now
Chemical Management Information
Stay updated with us
Sign Up for the Latest Updates
Stay informed about chemical supply chain disruptions and emerging innovations to keep your business at the forefront of efficiency and innovation. Uncover new ways to make your business practices more sustainable by incorporating safer products into your cleaning lineup.